The Gut-Brain Connection: How Nutritional & Functional Medicine Supports Mental Health and Wellbeing
Crafted by: Jonathan Chew
Introduction: How Your Gut Controls Your Brain
Ever wondered why you feel butterflies in your stomach before an important event? Or why stress can cause digestive issues? Science now confirms that the gut and brain are deeply connected through a complex communication system called the gut-brain axis.
📌 Did You Know?
✔ Over 90% of serotonin (the “happy hormone”) is produced in the gut.
✔ The gut contains over 100 million nerve cells, directly linking it to brain function.
✔ Gut inflammation has been linked to anxiety, depression, and cognitive decline.
💡 This means that if your gut is unhealthy, your brain will suffer too.
In this guide, we’ll explore:
✔ The science behind the gut-brain connection
✔ How gut imbalances contribute to anxiety & depression
✔ Functional Medicine strategies to improve mental health through gut health
✔ The best foods & nutrients for a healthy gut-brain axis
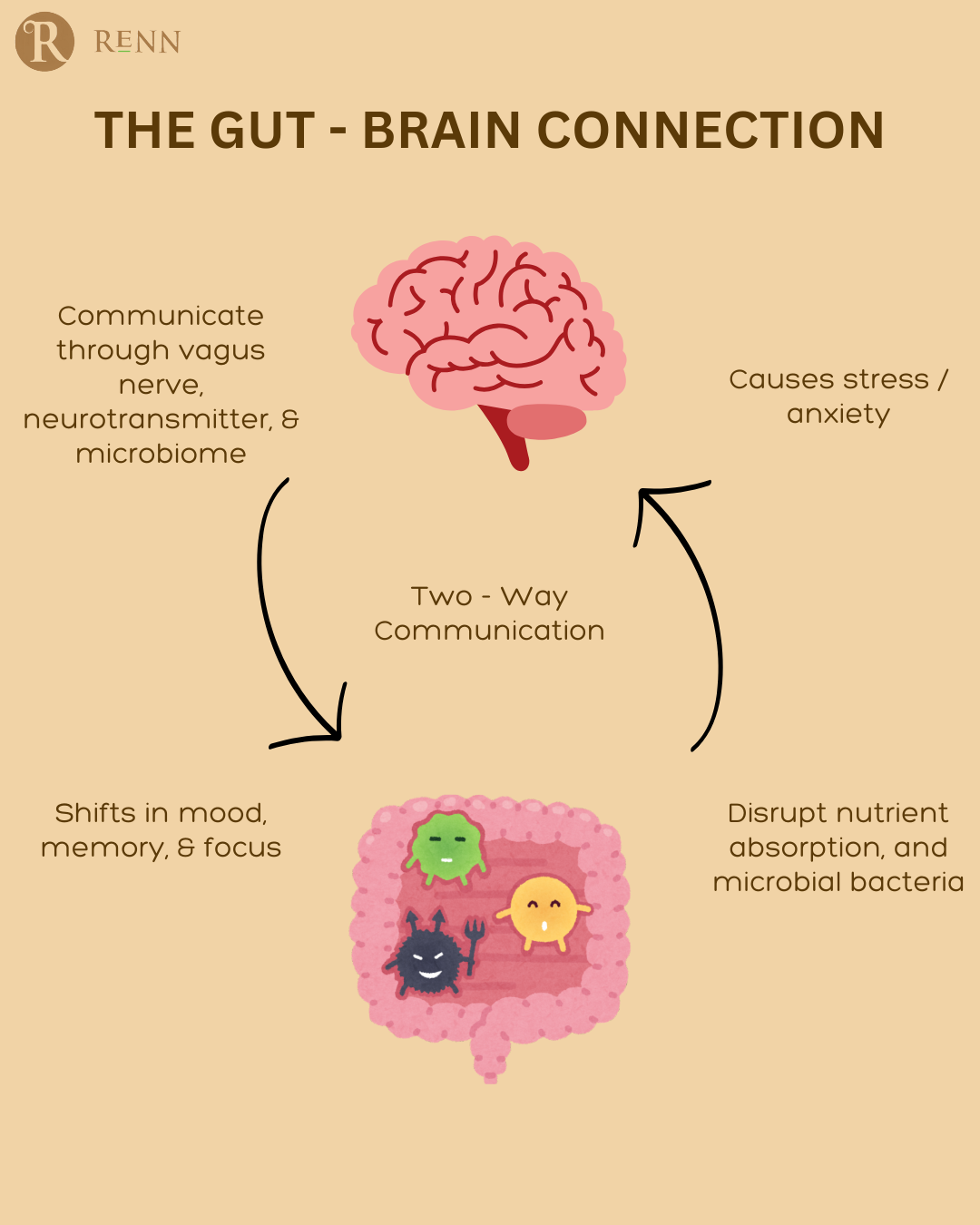
1️. What is the Gut-Brain Connection?
The gut and brain communicate through the vagus nerve, neurotransmitters, and the microbiome.
✔ Vagus Nerve: The “information highway” that connects the gut to the brain.
✔ Neurotransmitters: The gut produces key mood-regulating chemicals like serotonin, dopamine, and GABA.
✔ Microbiome Influence: A balanced gut microbiome supports mental clarity, emotional balance, and stress resilience.
🚨 What Happens When This Connection is Disrupted?
❌ Poor gut health leads to chronic inflammation, which negatively impacts mood, memory, and focus.
❌ An imbalance of gut bacteria can lead to low serotonin and dopamine, causing anxiety and depression.
❌ A damaged gut lining (leaky gut) allows toxins to enter the bloodstream, triggering brain fog and fatigue.
📌 Example: Studies show that people with gut dysbiosis (imbalanced gut bacteria) are more likely to experience depression and anxiety disorders.

2️. How Gut Health Affects Mental Health Conditions
Many mental health conditions have a hidden root cause in gut dysfunction.
🔹 1. Anxiety & The Gut
✔ Imbalanced gut bacteria can lead to excess cortisol (stress hormone), triggering anxiety.
✔ A lack of GABA (a calming neurotransmitter) is often linked to poor gut microbiome health.
✔ Probiotics and prebiotics can help regulate stress responses naturally.
📌 Functional Medicine Solution:
- Support gut bacteria with fermented foods & probiotics
- Use L-theanine & magnesium to calm the nervous system
- Avoid processed sugars, which worsen anxiety symptoms
🔹 2. Depression & Gut Inflammation
✔ Leaky gut and inflammation are linked to low serotonin production, worsening depression.
✔ Omega-3 fats, probiotics, and anti-inflammatory diets have been shown to boost mood.
✔ Studies show gut microbiome transplants can improve depression symptoms.
📌 Functional Medicine Solution:
- Eat an anti-inflammatory diet (rich in omega-3s, leafy greens, and turmeric)
- Heal the gut lining with collagen, glutamine, and bone broth
- Address nutrient deficiencies (B vitamins, zinc, magnesium, vitamin D)
🔹 3. Brain Fog & Cognitive Decline
✔ Toxins from an unhealthy gut can cross the blood-brain barrier, leading to poor focus and memory loss.
✔ Functional Medicine focuses on detoxifying the gut and supporting brain health naturally.
📌 Functional Medicine Solution:
- Optimize gut health with prebiotic & fiber-rich foods
- Remove processed foods and artificial additives
Boost brain nutrients like phosphatidylserine and acetyl-L-carnitine

3️. The Best Functional Medicine Strategies for a Healthy Gut-Brain Axis
A Nutritional & Functional Medicine approach to mental health focuses on:
🔹 1. Healing the Gut Lining
🚀 Goal: Prevent leaky gut & inflammation
✔ Consume collagen-rich foods (bone broth, gelatin)
✔ Take L-glutamine & zinc to repair gut lining
✔ Avoid processed foods & excessive alcohol
🔹 2. Supporting Beneficial Gut Bacteria
🚀 Goal: Balance microbiome for mental wellness
✔ Eat fermented foods (kimchi, kefir, miso)
✔ Take multi-strain probiotics
✔ Include prebiotics (fiber, garlic, onions, bananas)
🔹 3. Reducing Gut Inflammation
🚀 Goal: Lower systemic inflammation to boost brain function
✔ Follow an anti-inflammatory diet (Mediterranean-style)
✔ Use turmeric, ginger, and green tea
✔ Reduce processed sugar & gluten if sensitive
🔹 4. Optimizing Nutrient Intake for Mental Health
🚀 Goal: Support neurotransmitter production
✔ B vitamins & magnesium – Boost mood & calm the nervous system
✔ Omega-3 fatty acids (DHA & EPA) – Reduce anxiety & depression risk
✔ Polyphenol-rich foods (berries, dark chocolate, green tea) – Improve cognitive function
4️. How Functional Medicine Personalizes Gut-Brain Healing
Unlike conventional mental health treatments, Functional Medicine uses advanced diagnostics to customize a plan for each individual.
📌 Common Functional Medicine Tests for Gut-Brain Health:
✅ Comprehensive stool analysis (to assess microbiome balance)
✅ Organic acid testing (to check neurotransmitter function)
✅ Inflammation markers & food sensitivity testing
🚀 Example: Instead of just prescribing antidepressants, Functional Medicine practitioners may recommend gut-healing strategies alongside targeted supplements & dietary changes.
Conclusion: The Key to Mental Wellness Starts in the Gut
If you’ve been struggling with anxiety, depression, brain fog, or poor focus, the root cause might be in your gut.
📌 A Functional Medicine approach focuses on:
✅ Healing the gut to optimize neurotransmitter production
✅ Reducing inflammation to support brain health
✅ Balancing the microbiome for long-term emotional well-being
📞 Want to improve your mental health naturally?
📆 Schedule a consultation today to start your gut-brain healing journey!

