How Functional Medicine Can Complement Psychiatry for Mental Well-Being
Crafted by: Jonathan Chew

Introduction
Mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and mood imbalances, have traditionally been managed through psychiatric interventions such as pharmacotherapy and psychotherapy. While these approaches remain fundamental, the integration of Functional Medicine provides a holistic, evidence-based framework to optimize mental well-being. By addressing the biochemical and physiological factors underlying psychiatric conditions, Functional Medicine enhances treatment efficacy, improves patient outcomes, and contributes to sustainable mental health solutions.
The Biochemical Basis of Mental Well-Being
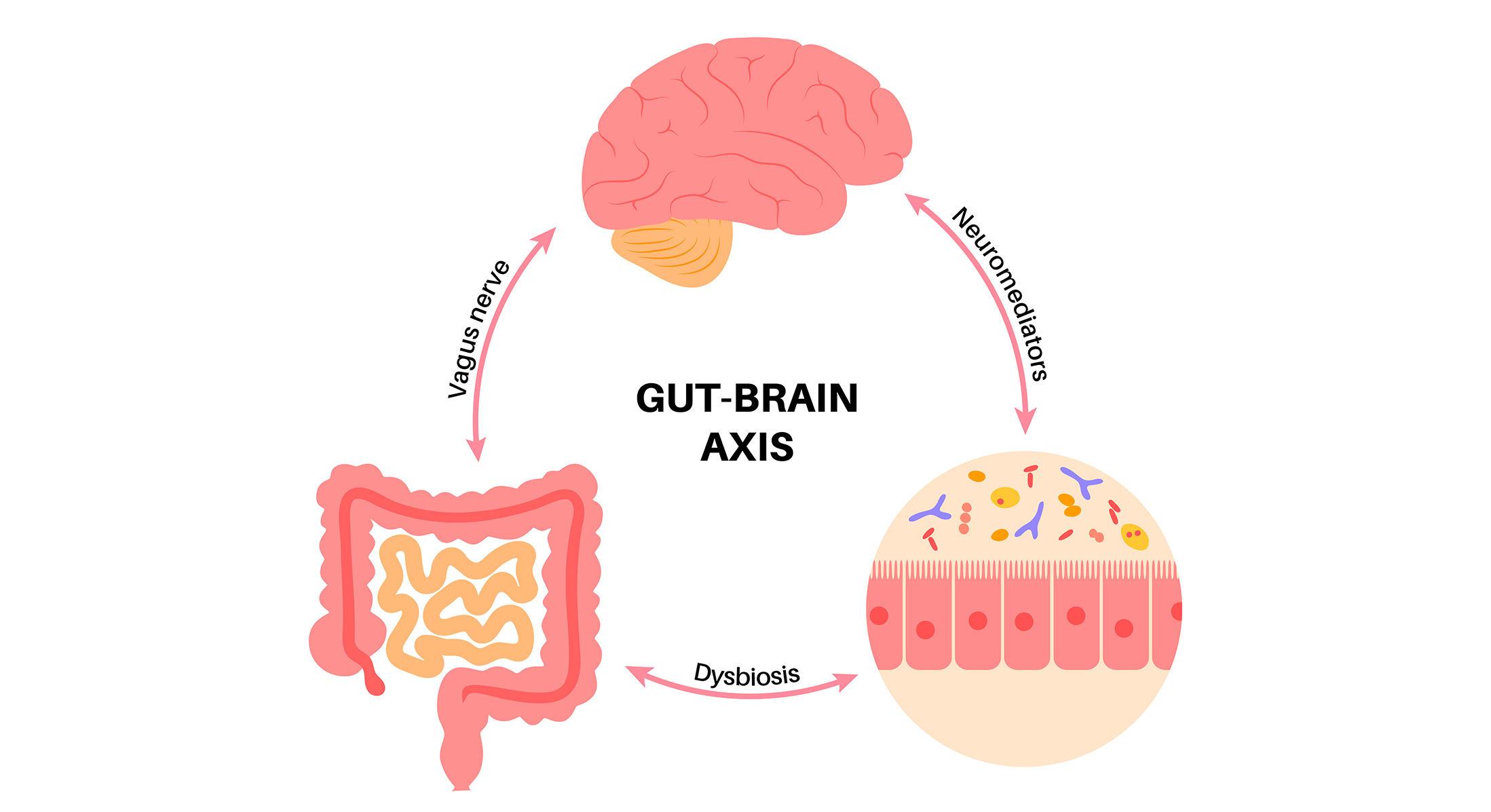
Mental health disorders often correlate with nutritional deficiencies, inflammation, gut dysbiosis, and metabolic dysfunctions. Emerging research has identified several key areas where Functional Medicine principles can support psychiatric care:
- Neurotransmitter Synthesis: Essential nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins (especially B6, B9, and B12), magnesium, and amino acids play crucial roles in neurotransmitter production (e.g., serotonin, dopamine, and GABA), which regulate mood and cognitive function.
- Gut-Brain Axis: The microbiome influences mental well-being through its role in neurotransmitter production, immune modulation, and inflammation control. Dysbiosis or leaky gut syndrome can contribute to anxiety and depression, making gut health restoration a priority.
- Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Elevated inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) have been linked to depression and other mood disorders. Anti-inflammatory interventions through dietary modifications and supplementation (e.g., curcumin, polyphenols, and antioxidants) can mitigate these effects.
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Energy Production: The brain requires substantial energy, and mitochondrial efficiency directly influences mental function. Coenzyme Q10, alpha-lipoic acid, and certain adaptogens (e.g., Rhodiola rosea) enhance mitochondrial function, improving cognitive resilience.
Key Functional Medicine Interventions for Mental Well-Being
Integrating Functional Medicine with psychiatric care involves a personalized approach, incorporating diagnostic assessments and targeted interventions. Below are key strategies:
I. Comprehensive Nutritional Assessment
A tailored assessment identifies deficiencies in essential micronutrients, amino acids, and fatty acids that impact brain function. Functional laboratory tests, including organic acid tests, serum vitamin and mineral levels, and gut microbiome analyses, provide insights for personalized treatment.
II. Dietary Modifications for Mental Well-Being
A nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory diet plays a pivotal role in mood regulation and cognitive stability:
- Mediterranean Diet: Rich in omega-3s, polyphenols, and fiber, supporting brain health and reducing inflammation.
- Ketogenic or Low-Carbohydrate Diets: Potentially beneficial for stabilizing mood disorders and enhancing brain energy metabolism.
- Elimination of Processed Foods and Allergens: Food intolerances and additives (e.g., artificial sweeteners, gluten, and dairy) can exacerbate psychiatric symptoms.
III. Targeted Supplementation
Based on individual biochemical needs, specific supplements enhance psychiatric care:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids (EPA/DHA): Proven to alleviate depression and improve cognitive function.
- B Vitamins & Magnesium: Crucial for neurotransmitter synthesis and nervous system regulation.
- Probiotics & Prebiotics: Supporting the gut-brain axis to improve mood and cognitive clarity.
- Adaptogenic Herbs (e.g., Ashwagandha, Rhodiola): Modulating stress response and resilience.
IV. Hormonal and Neurotransmitter Balance
Testing and addressing hormonal imbalances (e.g., thyroid function, cortisol dysregulation, and sex hormone deficiencies) are essential for individuals with treatment-resistant depression or anxiety. Amino acid therapy can further support neurotransmitter balance.
Integration of Functional Medicine with Psychiatry
Psychiatrists incorporating Functional Medicine principles can enhance patient care by:
- Identifying and correcting underlying metabolic and nutritional imbalances that may contribute to treatment resistance.
- Using a combined approach where medications are complemented with lifestyle and nutritional interventions to reduce side effects and improve efficacy.
- Monitoring biomarkers and personalizing treatments based on genetic, nutritional, and inflammatory profiles.
Conclusion
The integration of Functional Medicine with Psychiatry represents a paradigm shift toward precision mental health care. By addressing root causes, optimizing biochemical pathways, and personalizing interventions, this approach provides a synergistic framework for sustainable mental well-being. Future mental health care should move beyond symptom suppression and embrace a comprehensive, integrative model that enhances patient resilience, recovery, and long-term quality of life.

